The U.S. Sleep Crisis: Scientific Insights Into Why Millions Struggle to Sleep — and What Can Help
America is facing a growing sleep crisis driven by stress, technology, and biological disruption. Learn the science behind poor sleep and how Sleep Guard supports deeper, healthier rest.

📌 Introduction
Sleep is one of the most fundamental biological processes, yet millions of people in the United States struggle to get enough of it. The problem is so widespread that researchers now refer to it as a public health epidemic. According to national surveys, roughly 1 in 3 American adults experiences inadequate sleep, and more than 50 million are living with undiagnosed sleep disorders.
But why is sleep declining so dramatically?
Science has clear answers — and they point to a combination of psychological, biological, and lifestyle-driven factors.
Below is a comprehensive, research-backed look at the biggest sleep concerns affecting Americans today, why they happen, and what modern science says can support healthier sleep.
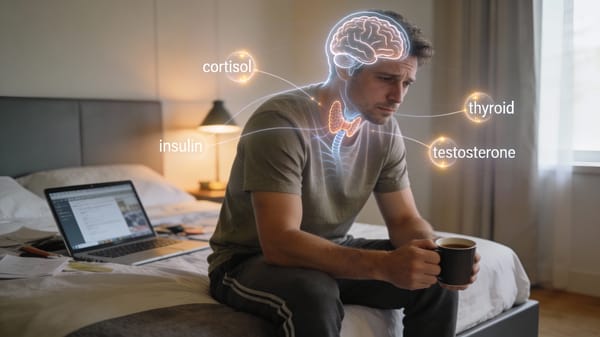
🧠 1. Stress, Cortisol, and the Hyperactive Brain
One of the most scientifically validated causes of sleep difficulty in the U.S. is elevated cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone.
🔬 What the science shows
Chronic stress keeps the brain in a state of hyperarousal — a condition where:
- The mind races at night
- The body remains alert instead of easing into sleep
- Sleep is lighter and more fragmented
- REM sleep (deep dreaming stage) is significantly reduced
Stress also disrupts the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, which controls the sleep–wake cycle. When this system stays activated, sleep becomes delayed, irregular, and less restorative.
📉 Real-life consequences
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Night-time awakenings
- Early morning waking
- Poor cognitive performance the next day
With financial pressure, digital overload, and societal demands rising, the American population is chronically overstimulated — and it’s sabotaging sleep.
📱 2. Blue Light & Circadian Rhythm Disruption
The human body operates on a 24-hour internal clock known as the circadian rhythm. Light is the key regulator of this system.
🔬 Why blue light is a problem
Screens emit short-wavelength blue light, which suppresses melatonin production by up to 80%. Melatonin is the hormone responsible for signalling the brain that it’s time to sleep. When melatonin drops:
- Sleep onset is delayed
- Deep sleep cycles shrink
- People wake feeling tired even after 7–8 hours
👁 Why this affects Americans more
The average U.S. adult spends 7+ hours per day on screens — much of it at night. Combined with fast-paced lifestyles and late-night entertainment culture, circadian rhythms are being shifted later than ever.
😴 3. The Rise of Insomnia and Other Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders are dramatically underdiagnosed in the U.S., even though they are extremely common.
✔ Common conditions include:
• Insomnia
Characterised by difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep. Often linked to anxiety, hyperarousal, and lifestyle patterns.
• Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
A disorder where airflow repeatedly stops during sleep, reducing oxygen and disrupting deep sleep stages.
• Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
Neurological condition causing uncomfortable sensations and leg movements that prevent sleep.
• Circadian rhythm disorders
Frequently seen in shift workers, students, and individuals with irregular schedules.
🔬 Biological impact
Sleep disorders reduce:
- Slow-wave sleep (the deepest, most restorative phase)
- REM sleep (crucial for memory and emotional regulation)
- Overnight hormonal balance
- Cardiovascular stability
And increase:
- Inflammation
- Insulin resistance
- Cognitive impairment
🛌 4. Chronic Sleep Deprivation: A National Pattern
Most adults need 7–9 hours of sleep. Yet millions consistently get less.
🔬 Sleep debt accumulates
The body cannot simply “catch up” on weekends. Accumulated sleep loss affects:
- Immune function
- Decision-making
- Mood regulation
- Hormonal balance
- Metabolism
Long-term sleep deprivation is linked to:
- Obesity
- Depression
- Cardiovascular disease
- Weakened immunity
- Cognitive decline
🧓 5. Ageing and Biological Changes in Sleep
As people age, sleep architecture changes naturally.
🔬 Age-related patterns
- Reduced melatonin production
- Shorter deep sleep cycles
- Increased night-time awakenings
- More medication interactions impacting sleep
This makes older adults especially vulnerable to chronic sleep issues.
🍷 6. Lifestyle Factors Americans Often Overlook
Several everyday habits subtly destroy sleep quality:
- Evening caffeine intake
- Alcohol before bed (reduces REM sleep)
- Irregular sleep schedules
- Heavy meals late at night
- Lack of daytime sunlight exposure
- Sedentary lifestyle
Individually, these seem small — but collectively, they significantly disrupt the sleep cycle.
💡 Why These Problems Are Worse in the U.S.
The U.S. has several unique social and environmental factors that amplify sleep struggles:
- “Always-on” work culture
- High stress and financial pressures
- High rates of screen use
- Long commutes and irregular schedules
- Environmental noise and artificial lighting
- High prevalence of obesity (linked to sleep apnea)
These create the perfect storm for a population suffering from chronic sleep imbalance.
🌙 The Solution Side: Science-Backed Ways to Improve Sleep
Improving sleep requires a combination of behavioural,, environmental, and sometimes nutritional strategies.
Research supports the following methods:
- Increasing morning light exposure
- Reducing screen time 1–2 hours before bed
- Lowering evening cortisol through relaxation techniques
- Improving sleep hygiene
- Regulating circadian rhythms
- Using evidence-supported natural supplements that promote calmness and melatonin balance
This leads us directly to a modern sleep-support option…
⭐ Introducing Sleep Guard — A Science-Aligned Approach to Better Sleep
After reviewing the biological and environmental factors behind the U.S. sleep crisis, it’s clear people need targeted support — not guesswork or harsh medications.
Sleep Guard is formulated to support the key scientific mechanisms behind healthy sleep:
✔ What Sleep Guard Is Designed to Support
1️⃣ Calming the nervous system
By supporting GABAergic and relaxation pathways, it helps reduce night-time hyperarousal — one of the biggest causes of insomnia.
2️⃣ Enhancing melatonin balance
Instead of forcing sleep artificially, it works with your body’s natural circadian rhythm.
3️⃣ Promoting deeper, more restorative sleep
Sleep Guard is designed to support slow-wave and REM cycles — essential for memory, recovery, and mental clarity.
4️⃣ Reducing night-time awakenings
By supporting hormonal balance and relaxation patterns it helps the brain maintain steadier sleep stages.
5️⃣ Supporting morning energy and mental clarity
Because the goal isn’t just sleep — it’s waking up refreshed.
📝 Final Thoughts
The United States is facing a sleep crisis driven by stress, screen habits, biological disruptions, and lifestyle factors. But science also tells us that with the right combination of habits and natural physiological support, sleep can be dramatically improved.
👉 Try Sleep Guard Plus and experience what real rest feels like.